
什么是LRU
LRU 缓存淘汰算法是一种常用缓存策略, LRU 全称是 Least Recently Used, 用于管理缓存中的数据。
工作原理:
- 【初始化】: 初始化一定 “容量” 的 [缓存管道], 当缓存溢出需要将最底部的数据移除
- 【访问数据】: 每次访问 (读或写) 缓存中的数据时, 将数据移到数据最顶部 (起始位) 或更新数据位置
- 【移除老旧数据】: 当缓存达到容量上限时, 需要移除最久并未访问过的数据, 即尾部数据
1 | const cache = new LRUcache(3) |
javascript中的Map
Map是一种数据结构, Map的键可以是任意类型的数据, 而我们可以借助 Map.prototype.keys 实现.
先看 Map.keys 能拿到什么
这时可以拿到 Map迭代器 , 我们知道迭代器 iterator 有 next 方法, 每次调用都会返回一个包含 value, done 的对象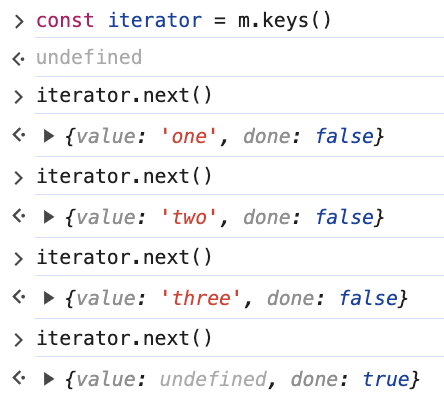
这时我们可以利用Map自身api及iterator.next返回的键值对实现LRU
LRU
直接看代码:
1 | class LRUCache { |